Runoff
|
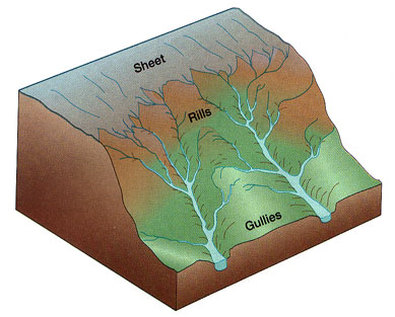
Moving water is the major cause of erosion that shaped earths surface. Erosion by water begins with a drop of rain. Some water from the rain is evaporated or soaked up by plants other parts of the rain sinks into the soil. As it starts to rain the force of a raindrop can pick up and loosen soil particles. As the water travels it takes the soil particles with it. This water that travels across the land is called runoff. As runoff flows over the land it can cause a type of erosion called sheet erosion.
The amount of runoff will vary from the type of land. There are five different factors to the amount of runoff. The first factor is vegetation. Vegetation such as trees, shrubs, and grass absorb the water reducing the amount of runoff. The second factor is the amount of rainfall an area has. An area with lots of rainfall have less runoff and erosion because there are more plants to absorb it and protect the soil from erosion. The third factor is the type of soil. Some soils absorb more water than others, the more water absorbed the less runoff. The fourth factor is the shape of the land. For runoff to travel it has to be on a slope to be pulled by gravity downhill, therefore making it harder for runoff to flow on flat land. The last factor is how the land is used. For example a paved road does not absorb any water, making all the water that hits its surface runoff. |
|
Rills and Gullies
|
As runoff travels across land it creates small grooves in the soil. These small grooves are called rills. As more and more rills are created they join together to make bigger rills in the soil. Once these rills become bigger they are called gullies. Rills and gullies can only contain water in them after it rains. As the gullies carry water the water picks up soil and rock and erode the sides making the gully larger.
|
Streams and Rivers
|
Once gullies start to combine together they become a stream. A stream is a channel that water continuously flows downhill. Streams rarely ever dry up. A smaller stream can be called a creek or a brook. As streams flow the water erodes the sides of the stream making it larger, streams can also flow together and become larger. Larger streams can be called rivers.
|
Tributaries
|
A tributary is a stream or river that connects to another larger stream or river. Tributaries help water flow into rivers. A tributary gets its water from a water basin or a watershed. For example the amazon river has 29 different tributaries, two of which are called the Curaray river and the Tambo river.
|
Erosion by Rivers
|
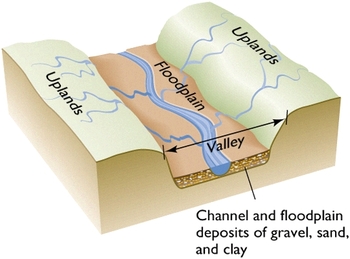
Through erosion a river can create many land forms such as valleys, waterfalls, flood plains, meanders and oxbow lakes. Rivers usually form on steep mountains and slopes. Near a rivers source it flows fast and flows in a straight line downhill. As the the river erodes the sides of the slope it creates a V-shaped valley.
|
Waterfalls
|
Once a stream or river come to a place where the rock is hard and doesn't erode as easy, the river may flow over that rock and then come to softer rock down stream. As the river flows over both types of the rock the softer rock erodes faster. Eventually the softer rock comes to a point where it is removed and there is a steep drop, creating a waterfall. In areas where water looks rough it is called rapids. Rapids can sometimes occur the same way waterfalls do.
|
Flood Plains
|
A flood plain is the flat wide area along a river. When a river gets closer to the end of its source it flows over gentle slopes. As the river flows it becomes wider and erodes more land, as it gets bigger it creates a river valley making the land flat and creating a flood plain. when the flood plane is wide the walls can be kilometers away from the river.
|
Meanders
|
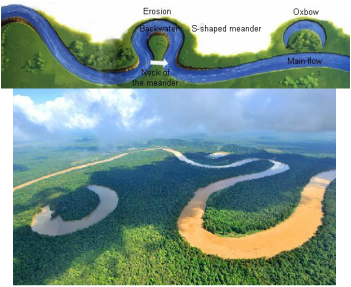
A meander is a bend that almost forms a loop in the coarse of a river. A meander is usually very deep and wide. A meander occurs when a river flows through rock that can easily be eroded. As the meander curves, the water erodes the outer side of the bank and deposits that sediment on the inner side of the bank, because the meander erodes the outside of the bank so much the sediment that the river carries can erode a flood plain.
|
Oxbow Lake
|
An oxbow lake is a meander that is no longer attached to the river. When a river floods the water has to find a straighter route downstream, so the water flows over the ends of the meander. As the flood starts to to go down, the water deposits sediment and covers up the ends of the meander making an oxbow lake.
|
Deposits by Rivers
|
As a river moves it erodes rock and takes the pieces of sediment it eroded with it downstream. When a river slows down it deposits sediment, small particles are dropped and larger sediment such as stones quit rolling. Deposition by rivers can form alluvial fans, deltas, and can add soil to flood plains.
|
Alluvial Fans
Deltas
|
A delta is a landform created when a river deposits sediment where it flows into a body of water. A rivers coarse ends when it is dumped into still water such as an ocean, and because the water is no longer flowing the sediment it was carrying is deposited, creating a delta. Deltas may vary in many shapes and sizes.
|
Soil Deposited on Flood Plains
Heavy rain and the melting of snow and ice can cause a river to flood. When a river floods it flows over its flood plain. When the flood goes down the sediment is deposited on the flood plain. This is what makes some flood plains so fertile. Some flood planes can grow dense forests or even crops.
Groundwater Erosion
|
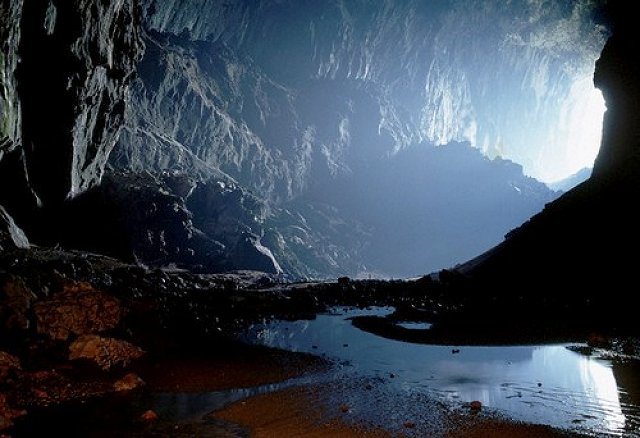
Groundwater is underground water that helps shape the land. When it rains not all rain water becomes runoff, it also can be soaked into the ground. Once the water is soaked up it fills in the cracks of soil and rock. Groundwater can sometimes cause erosion through processes of chemical weathering. When the water combines with acid it creates carbonic acid. Once the carbonic acid is created, it flows in cracks of limestone. The carbonic acid changes the limestone chemically and the limestone is carried away by water. This process slowly hollows out rocks and overtime develops into large underground caves.
|
Cave Formations
|
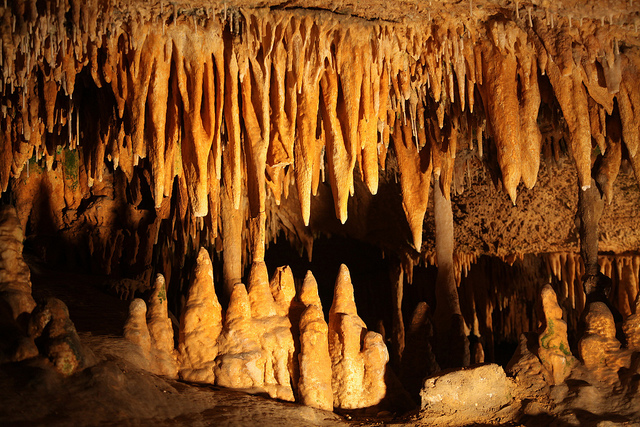
Once the the limestone is carried away with the soultion of water it is capable of creating stalagmites and stalactites. A stalagmite is a cone shaped deposit of limestone building up on the ground of a cave. A stalactite is a cone shaped deposit of limestone hanging from the roof of a cave. Stalagmites and stalactite are formed when carbonic acid, mixed with water and limestone drip from a cave roof.
|
Karst Topography
|
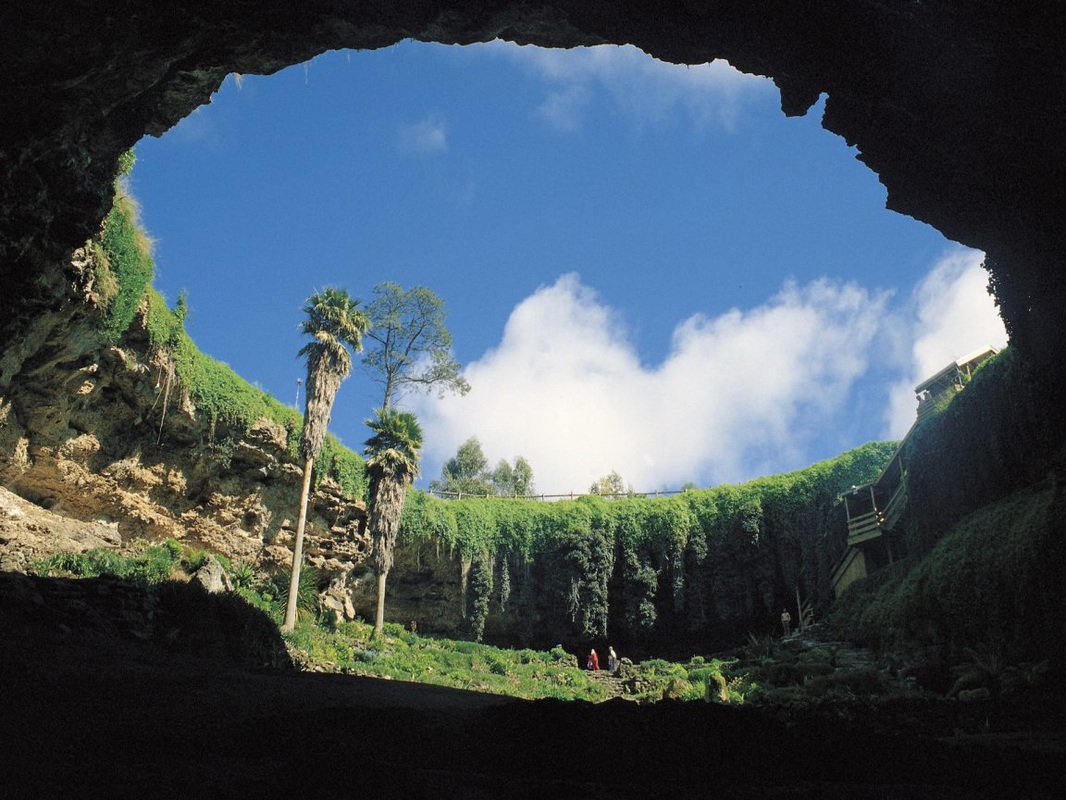
Karst topography is a layer of limestone close to the surface that creates deep valleys, caverns, and sinkholes. In an area where this limestone near the surface, groundwater erosion can change the shape of the land. In these areas, streams are rare because water sinks into the limestone. When the roof of a cave collapses, the result is a sinkhole. This creates karst topograghy.
|