How Glaciers Form
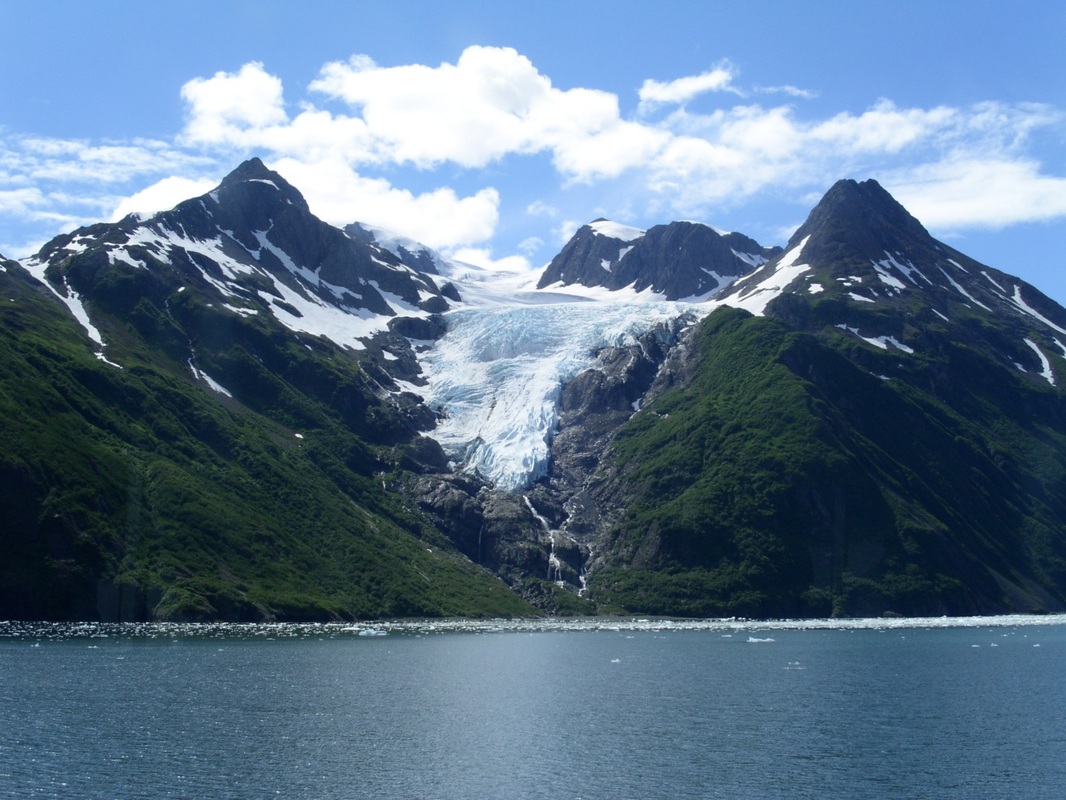
Valley Glaciers
Continental Glaciers
|
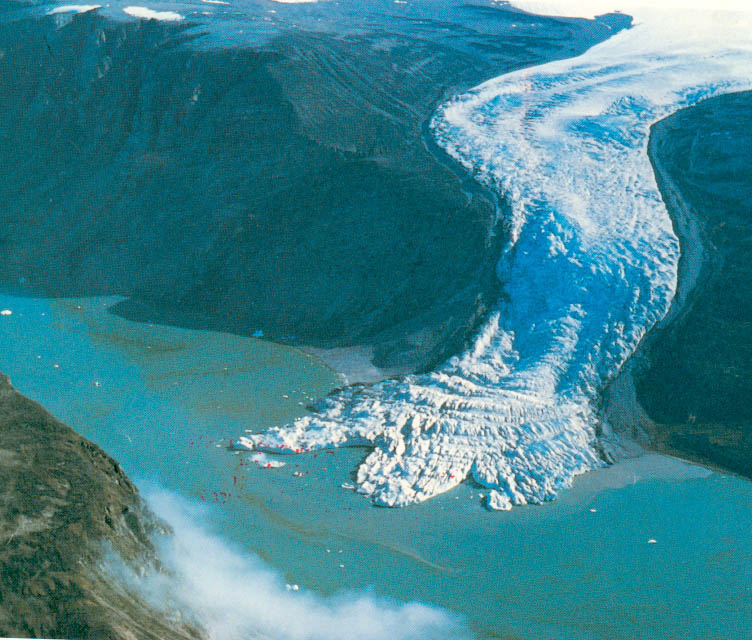
A continental glacier covers most of a continent or a large island. Continental glaciers can be hundreds of square kilometers long and wide. Continental glaciers aren't restricted of any movement, so the glacier can move in all directions. About 10% of earths surface is covered by a continental glacier. At one point more than 10% was covered, during these times it was called the ice age.
|
How Glaciers Move
|
Glaciers can only form in a place where more snow falls than melts. As snow starts to build up glaciers get taller and taller. Once the glacier reaches 30 to 40 meters tall gravity starts to pull the glacier downhill. A glacier can be pulled up to a few centimeters to a few meters per day. Sometimes a glacier starts to slide. When a glacier slides it is called surging. After a year of slipping and sliding a glacier can reach up to 6 kilometers.
|
Glacier Erosion
|
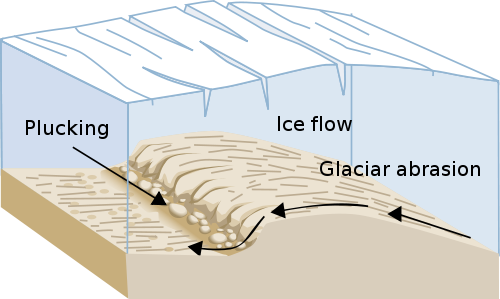
Glaciers erode the land in two ways, by plucking and abrasion. Plucking is the process when a glacier picks up rocks. The weight of a glacier makes it easy to break rocks and boulders in pieces. Once all the rocks fragments are picked up they are carried around wherever the glacier goes. As the glacier moves along the land the rock fragments that were stuck to the bottom scrap against the bedrock, causing abrasion.
|
Glacial Deposition
|
Once the glacier starts to melt all the sediment that was picked up is deposited. The sediment that is deposited by a glacier is called till. As the till is deposited it can create different landforms. The till that is deposited from the sides of the glaciers are called a moraine. The side of the moraine that has reached the farthest length is called the terminal moraine. As the glacier retreats it can create a kettle. A kettle is a small depression in the ground that forms when a chunk of ice is left in the till. Once a kettle is formed it fills up with water creating a small pond or lake. These ponds or lakes are called a kettle lake.
|